316 / 316L Stainless steel pipe VS 304 / 304L stainess steeel pipe

316/316L Stainless Steel Pipe: Properties, Applications, and Advantages
316/316L stainless steel pipe is an austenitic stainless steel alloy that is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, mechanical properties, and versatility. It is a popular choice for various industries, including marine, chemical processing, pharmaceutical, and food and beverage. In this article, we will explore the properties, applications, and advantages of 316/316L stainless steel pipes.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Composition of 316/316L Stainless Steel
Mechanical Properties
Corrosion Resistance
Heat Resistance
Fabrication
Applications
Advantages
Conclusion
Introductior
316 stainless steel is an austenitic stainless steel alloy containing 16-18% chromium, 10-14% nickel, and 2-3% molybdenum by weight. The addition of molybdenum significantly enhances its corrosion resistance, particularly in chloride-containing environments. 316L is a low carbon variant of 316 stainless steel, with a maximum carbon content of 0.03%. This lower carbon content helps prevent sensitization (the formation of chromium carbide precipitates at grain boundaries) during welding and improves its corrosion resistance.

|
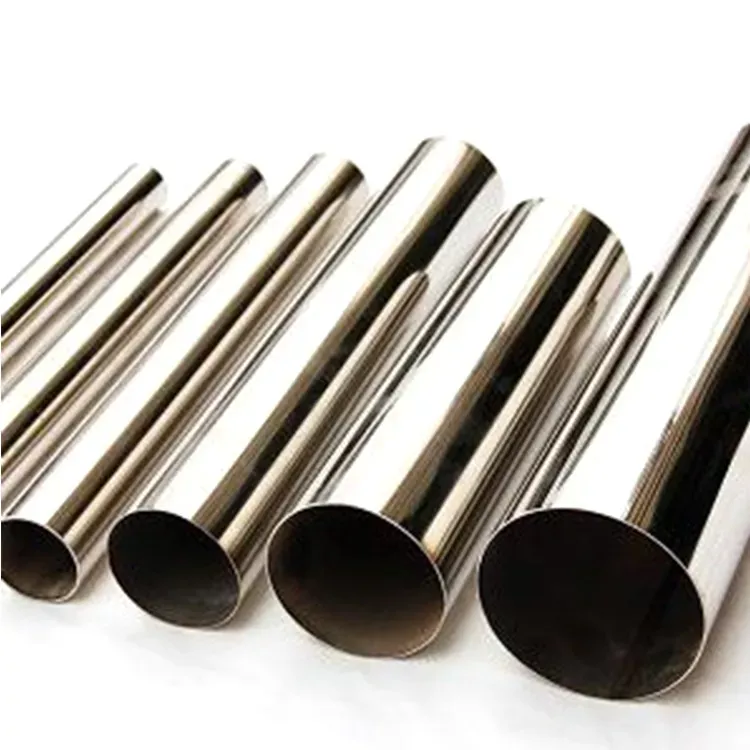
Stainless steel round tube
|
|
|
Steel Grade
|
302, 303,303Cu, 304, 304L, 304H, 310S, 316, 316L, 317L, 321,310S
309S, 410, 410S,420, 430, 431,
4L
|
|
Standard
|
ASTM A240/A240M, ASME SA- 240/SA-240M, JIS G 4305,
EN10028-7, EN10088-2
|
|
Wall thickness
|
1mm-150mm
|
|
Outer diameter
|
6mm-2500mm
|
|
Length
|
2000mm-6000mm
|
|
deviation
|
≤0.1%
|

|
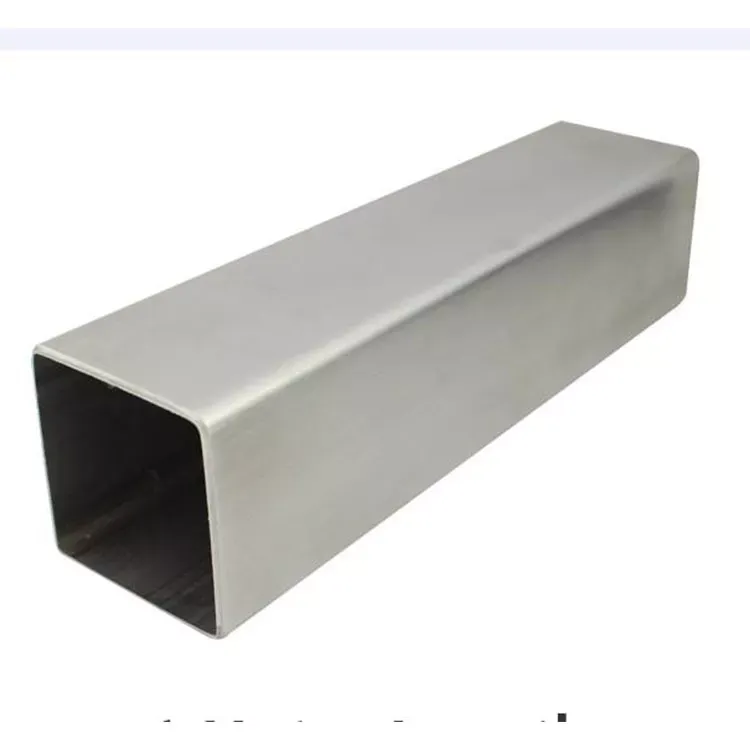
Stainless steel square tube
|
|
|
Steel Grade
|
302, 303,303Cu, 304, 304L, 304H, 310S, 316, 316L, 317L, 321,310S 309S, 410, 410S,420, 430, 431, 4L
|
|
Standard
|
ASTM A240/A240M, ASIffi SA-240, SA-24OM, JIS G 4304, EN 10028-
7, EN 10088-2
|
|
Wall thickness
|
1mm-150mm
|
|
Outer diameter
|
6mm-2500mm
|
|
Length
|
2000mm–6000mm
|
|
deviation
|
≤0.1%
|

|
Stainless steel welded pipe
|
|
|
Steel Grade
|
302, 303,303Cu, 304, 304L, 304H, 310S, 316, 316L, 317L, 321,310S 309S, 410, 410S,420, 430, 431, 4L
|
|
Standard
|
ASTM A240/A240M, ASIffi SA-240, SA-24OM, JIS G 4304, EN 10028-7, EN 10088-2
|
|
Wall thickness
|
1mm-150mm
|
|
Outer diameter
|
6mm-2500mm
|
|
Length
|
2000mm–6000mm
|
|
deviation
|
≤0.1%
|



316/316L Stainless Steel Pipe vs 304/304L Stainless Steel Pipe: A Comprehensive Comparison
Stainless steel pipes are widely used in various industries due to their corrosion resistance, durability, and high strength. Two popular grades of stainless steel, 304/304L and 316/316L, are often compared to determine the best-suited material for a project. In this article, we will delve into the differences, similarities, and applications of these two stainless steel grades.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Composition of 304/304L and 316/316L Stainless Steel
- Mechanical Properties
- Corrosion Resistance
- Heat Resistance
- Fabrication
- Cost and Availability
- Applications
- Conclusion
1. Introduction
Both 304/304L and 316/316L stainless steel pipes are part of the 300 series austenitic stainless steel family. Austenitic stainless steel is known for its excellent formability, weldability, and toughness. The 300 series is the most commonly used type of stainless steel, accounting for over 70% of global stainless steel production.
1.1. 304/304L Stainless Steel
304 stainless steel is the most widely used stainless steel grade and is often considered the standard “18-8” stainless steel. It contains 18% chromium and 8% nickel by weight. 304L is a low carbon variant of 304, with a maximum carbon content of 0.03%. This lower carbon content helps prevent sensitization (the formation of chromium carbide precipitates at grain boundaries) during welding and improves its corrosion resistance.
1.2. 316/316L Stainless Steel
316 stainless steel is similar to 304 stainless steel but contains an additional element, molybdenum. This addition increases its resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion in chloride-containing environments. 316L is a low carbon variant of 316 stainless steel, with a maximum carbon content of 0.03%. Like 304L, this lower carbon content helps prevent sensitization during welding and improves corrosion resistance.
2. Composition of 304/304L and 316/316L Stainless Steel
The chemical compositions of 304/304L and 316/316L stainless steel are listed in the table below:
| Element | 304/304L (%) | 316/316L (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon (C) | ≤ 0.08 / ≤ 0.03 | ≤ 0.08 / ≤ 0.03 |
| Chromium (Cr) | 18.00 – 20.00 | 16.00 – 18.00 |
| Nickel (Ni) | 8.00 – 10.50 | 10.00 – 14.00 |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | – | 2.00 – 3.00 |
| Manganese (Mn) | ≤ 2.00 | ≤ 2.00 |
| Silicon (Si) | ≤ 0.75 | ≤ 0.75 |
| Phosphorus (P) | ≤ 0.045 | ≤ 0.045 |
| Sulfur (S) | ≤ 0.030 | ≤ 0.030 |
As evident from the table, the main difference in the compositions of 304/304L and 316/316L stainless steel is the presence of molybdenum in the latter. This added element enhances the corrosion resistance of 316/316L stainless steel, especially in chloride-containing environments.
3. Mechanical Properties
The mechanical properties of stainless steel pipes are crucial in determining their suitability for specific applications. Here, we compare the mechanical properties of 304/304L and 316/316L stainless steel.
| Property | 304/304L | 316/316L |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 515 MPa (75 ksi) / 485 MPa (70 ksi) | 515 MPa (75 ksi) / 485 MPa (70 ksi) |
| Yield Strength | 205 MPa (30 ksi) / 170 MPa (25 ksi) | 205 MPa (30 ksi) / 170 MPa (25 ksi) |
| Elongation | 40% / 40% | 40% / 40% |
| Hardness (Brinell) | ≤ 201 / ≤ 201 | ≤ 217 / ≤ 217 |
As the table shows, the mechanical properties of 304/304L and 316/316L stainless steel pipes are quite similar. This makes both grades suitable for a wide range of applications where high strength and toughness are required.
4. Corrosion Resistance
One of the primary reasons for choosing stainless steel is its corrosion resistance. The addition of molybdenum in 316/316L stainless steel provides it with improved corrosion resistance, particularly in chloride-containing environments.
4.1. General Corrosion
Both 304/304L and 316/316L stainless steel pipes have excellent general corrosion resistance. However, in more aggressive environments, such as those with high chloride or acidic content, 316/316L is the superior choice due to the presence of molybdenum.
4.2. Pitting and Crevice Corrosion
Pitting and crevice corrosion are forms of localized corrosion that occur in chloride-containing environments. The molybdenum in 316/316L stainless steel significantly increases its resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion compared to 304/304L. This makes 316/316L a more suitable choice for applications in marine and chemical processing environments.
4.3. Stress Corrosion Cracking
Stress corrosion cracking (SCC) is a form of corrosion that occurs in environments with a combination of tensile stress, high temperatures, and specific corrosive agents. Both 304/304L and 316/316L stainless steel pipes have good resistance to SCC. However, 316/316L may provide better resistance in certain chloride-rich environments.
5. Heat Resistance
Heat resistance is another important factor when selecting stainless steel pipes. Both 304/304L and 316/316L stainless steel pipes have good oxidation resistance up to 870°C (1600°F). However, continuous exposure to temperatures above 425°C (800°F) can lead to carbide precipitation in 304 stainless steel, reducing its corrosion resistance. The low carbon content in 304L and 316L stainless steel pipes reduces the risk of carbide precipitation, making them suitable for high-temperature applications.
6. Fabrication
Fabrication characteristics, such as formability and weldability, are essential when selecting stainless steel pipes for a project. Both 304/304L and 316/316L stainless steel pipes have excellent formability and can be easily formed into various shapes. They can also be readily welded using most common welding techniques, with 304L and 316L being preferred for their reduced risk of sensitization.
7. Cost and Availability
Cost and availability are important factors when choosing between 304/304L and 316/316L stainless steel pipes. Due to the higher nickel and molybdenum content, 316/316L stainless steel pipes are generally more expensive than 304/304L. However, the cost difference is often offset by the improved corrosion resistance and performance of 316/316L in specific environments. Both grades are readily available in various forms and sizes.
8. Applications
The choice between 304/304L and 316/316L stainless steel pipes depends on the specific requirements and environmental conditions of a project. Some typical applications for each grade include:
8.1. 304/304L Stainless Steel
- Food processing equipment
- Kitchen appliances and utensils
- Architectural panels and railings
- Chemical containers and storage tanks
- Heat exchangers and piping systems
8.2. 316/316L Stainless Steel
- Marine environments and applications
- Chemical processing equipment
- Pharmaceutical and biotechnology equipment
- Pulp and paper processing equipment
- Coastal and high-chloride environments
9. Conclusion
In conclusion, both 304/304L and 316/316L stainless steel pipes are versatile materials with a wide range of applications. While they share several similarities in terms of mechanical properties and fabrication characteristics, the key difference lies in their corrosion resistance. The presence of molybdenum in 316/316L stainless steel provides it with superior corrosion resistance, especially in chloride-containing environments. Ultimately, the choice between the two grades will depend on the specific requirements and environmental conditions of the project.