Concrete Weight Coating Pipe | CWC | Concrete Coated Pipe
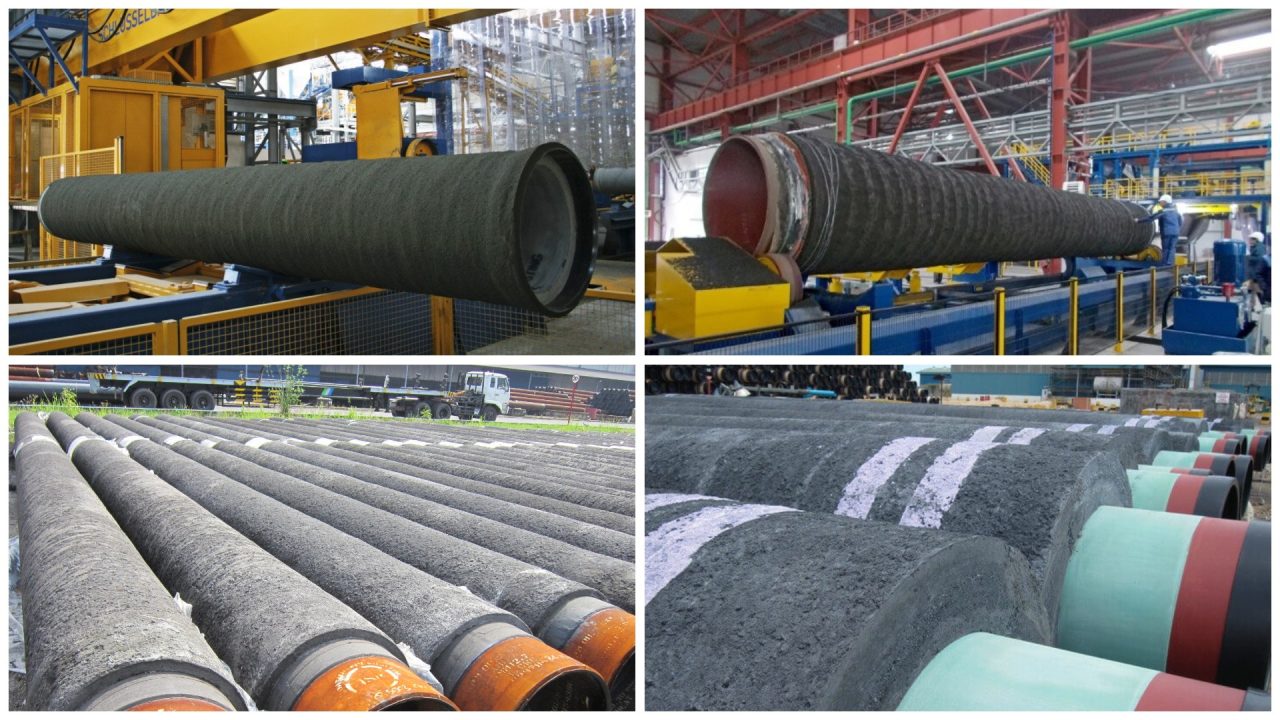

What is The Concrete Weight Coating (CWC) Pipe
Concrete weight coating (CWC) is a type of coating used primarily for underwater steel pipelines to provide negative buoyancy (i.e., making the pipe sink in water) and mechanical protection. It also offers a degree of thermal insulation. The concrete coating can be applied over a layer of anti-corrosion coating such as Fusion Bonded Epoxy (FBE), 3LPE (3-layer polyethylene), or 3LPP (3-layer polypropylene) to ensure that the steel pipe is protected from the corrosive underwater environment.
ABTER STEEL provides different types of concrete weight coating (CWC) pipes as follows:
Pipe diameter: 152.4 mm – 1524 mm (6” – 60”)
Pipe thickness: SCH 20, SCH 40, SCH 80, etc.
Applicable standard (steel pipe): API 5L Grade B to Grade 80, ISO 3183 Grade L245 to L555, GB, etc.
Pipe length: Up to 12 meters
Concrete density: 1.8 ton/ m3 – 3.5 ton/ m3 (Concrete formulation can be tailor-made to any specified density as per client requirement)
Concrete thickness: 25 mm – 200 mm
Concrete compressive strength: Up to 50 Mpa
Key features of concrete weight coating (CWC) pipe
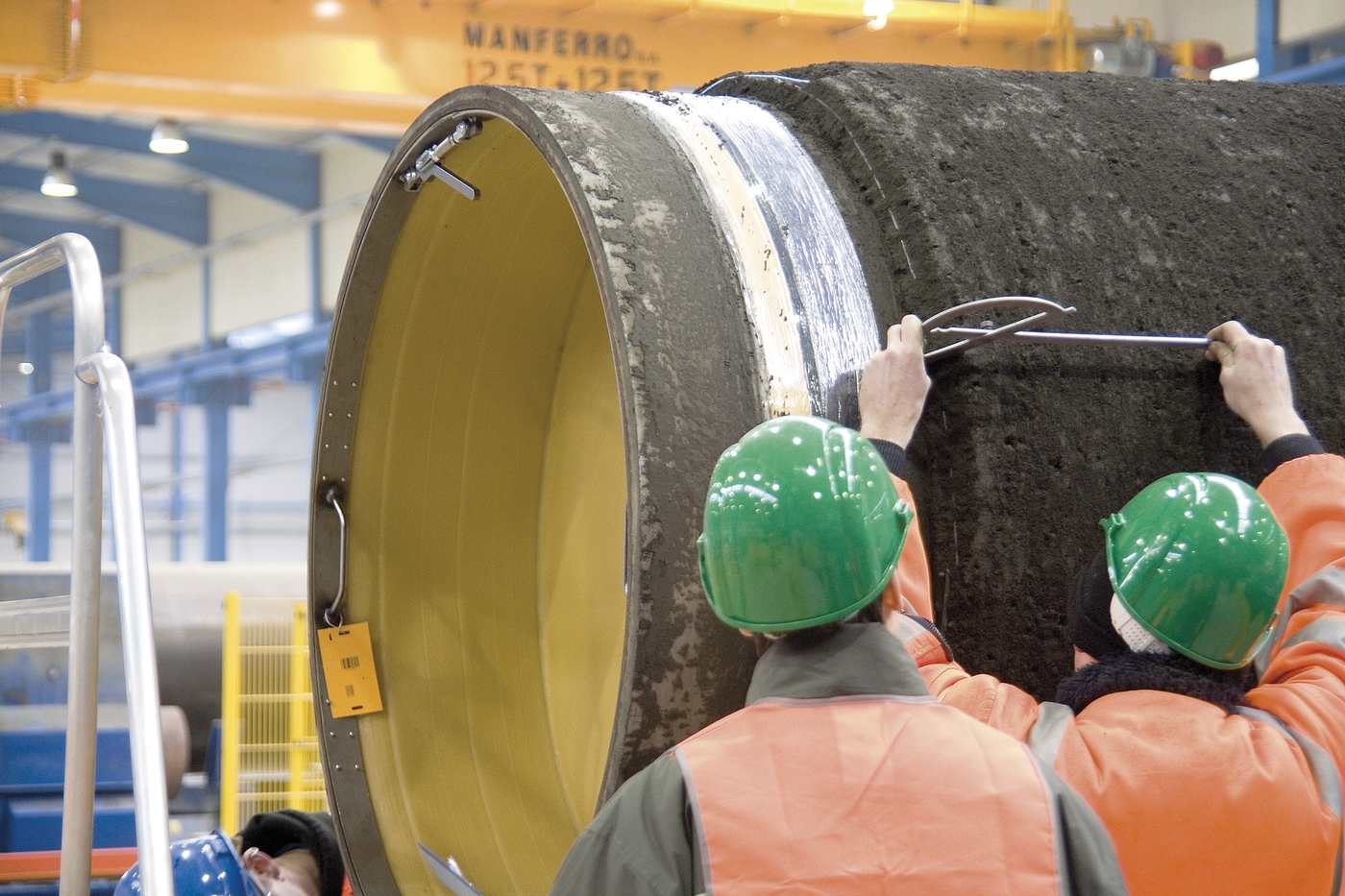

Structure
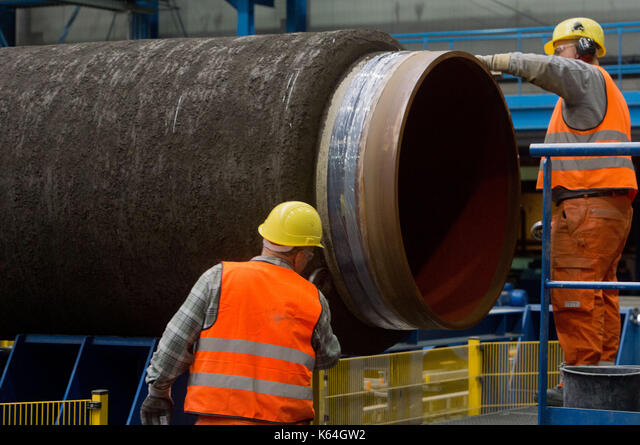

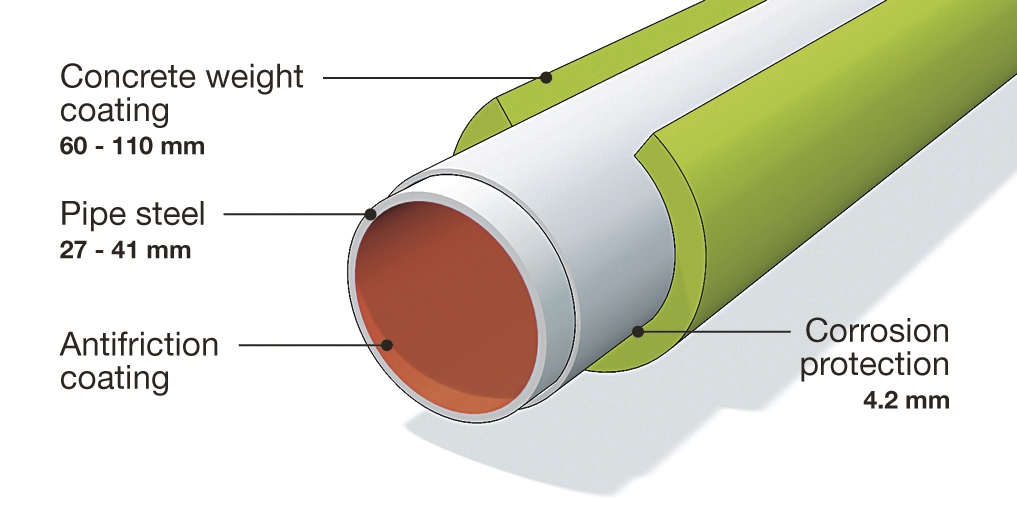
The CWC pipe typically consists of the following layers:
- Steel Pipe: The primary conduit for the transport of materials.
- Anti-Corrosion Coating: A layer of anti-corrosion coating (such as FBE, 3LPE, or 3LPP) is applied on the steel pipe to protect it from corrosion.
- Reinforcement Layer: This layer, often made of felt or fabric, is applied over the anti-corrosion coating to protect it during the application of the concrete coating.
- Concrete Coating: The outermost layer is a thick layer of concrete that provides negative buoyancy and mechanical protection.
Process
The process of applying the concrete weight coating is as follows:
- Surface Preparation: The pipe surface is prepared by removing any dirt, rust, or mill scale.
- Anti-Corrosion Coating Application: An anti-corrosion coating is applied on the pipe.
- Reinforcement Layer Application: A reinforcement layer is applied over the anti-corrosion coating.
- Concrete Coating Application: The concrete coating is applied over the reinforcement layer. This is typically done by spraying the concrete onto the pipe in a controlled manner.
- Curing: The coated pipe is then allowed to cure until the concrete has hardened.
Applications
CWC pipes are primarily used in the oil and gas industry for the laying of underwater pipelines. They are also used in other applications where pipes need to be sunk underwater, such as in offshore wind farms.
Advantages
- Negative Buoyancy: Ensures that the pipe sinks and remains stable at the seafloor.
- Mechanical Protection: Protects the pipe from physical damage during installation and service.
- Thermal Insulation: Offers a degree of thermal insulation, reducing heat loss in hot fluid transportation.
- Corrosion Protection: When applied over an anti-corrosion coating, it provides protection from the corrosive underwater environment.
Standards
The application of concrete weight coating on pipes is guided by international standards such as:
- ISO 21809-5: Petroleum and natural gas industries — External coatings for buried or submerged pipelines used in pipeline transportation systems — Part 5: External concrete coatings.
- DNVGL-ST-F101: Submarine pipeline systems (previously DNV-OS-F101), which gives requirements for submarine pipeline systems, including CWC.
Concrete weight coating pipe consist of cement, water, aggregates and reinforcement materials, the advantage of CWC pipe is to fix the pipeline stably performances and provides effective mechanical protection. Compared with other insulation type like pipe-in-pipe double-layer steel pipe structure, CWC pipe is more efficient in saving cost, easy the pipeline installation and convenient the operations.
Key Notes During Concrete Weight Coating (CWC) Pipe Manufacturing Processes
Producing concrete weight coated (CWC) pipes involves a series of steps, and there are key considerations at each stage to ensure a successful application. Here are some of the most important notes:
1. Pipe Surface Preparation
The steel pipe surface should be thoroughly cleaned to remove any oil, grease, dirt, scale, or rust. The surface preparation is crucial for the adhesion of the subsequent layers.
2. Anti-Corrosion Coating
The pipe is then coated with an anti-corrosion layer. This layer should be uniformly applied and free from defects, as it plays a crucial role in protecting the pipe from corrosion.
3. Reinforcement Layer
A reinforcement layer is applied over the anti-corrosion coating. This layer provides mechanical protection for the anti-corrosion coating during the concrete coating application and should be properly adhered to the anti-corrosion layer.
4. Concrete Coating
The concrete used for the coating should have the right mix of cement, aggregate, and water, and should be prepared as per the standard specifications. The concrete should be applied uniformly over the pipe to ensure even weight distribution. The thickness of the concrete layer should be as per the design specifications.
5. Curing
The coated pipe should be allowed to cure in a controlled environment. The curing time can vary depending on the type of concrete used and the environmental conditions. The curing process is critical for the concrete to reach its desired strength.
6. Inspection and Testing
Every stage of the process should be monitored and tested. Inspections should be carried out to ensure that each layer is applied correctly and free from defects. Non-destructive testing methods can be used to check the integrity of the coatings.
7. Handling and Transportation
Proper care should be taken while handling and transporting the coated pipes. Any damage to the coating can lead to exposure of the steel pipe to corrosive elements.
It’s important to remember that all these steps need to be carried out as per the relevant industry standards and specifications. These standards will provide detailed guidelines on the materials, processes, testing, and inspection procedures.